Causal Ambiguity Definition Business
Causal Ambiguity is in decision making and strategy formation the situation where it is hard or even impossible to relate the consequences or effects of a phenomenon to its initial states or causes. It is the uncertainty due to the quality of being open to more than one interpretation of the relationship between 2 phenomena like for example between the resources a company has.
At the extreme ambiguity may be so great that not even managers within the firm under-stand the relationship between actions and out-comes.

Causal ambiguity definition business. In other words people prefer making a bad decision where all information is known to making a good decision that involves missing information. It is the basic ambiguity concerning the nature of the causal connections between actions and results p. It is argued that tacitness complexity and specificity in a firms skills and resources can generate causal ambiguity in competency-based advantage and thus raise barriers to imitation.
Powell Lovallo Caringal 2006. The strategy is quite unique as most companies who succeed as a result of causal. Causal ambiguity is defined as the uncertainty that stems from a basic ambiguity concerning the nature of the causal connections between actions and results Lippman and Rumelt 1982 p.
The situation where an effect occurs but the exact cause is not known. Lippman and Rumelt 1982 p. Barneys 1991 article Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage is widely cited as a pivotal work in the emergence of the resource-based view.
Being a good business person is about making more right decisions than you do wrong. Get comfortable with making mistakes by looking at them as learning opportunities. The ambiguity effect has numerous business implications for sales marketing employee motivation and decision making.
The ambiguity effect is a bias for perfect information in decision making. Causal ambiguity has been defined as the basic ambiguity arising from the nature of the causal connexions between actions and results Lippman Rumelt 1982. But is phenomenon is also very common in strategy where it is often impossible to determine whether the.
Dont let that put you off. Up to 10 cash back More recently causal ambiguity has also been viewed as an intra-firm phenomenon that can limit the extension of a competitive advantage because of the difficulty of replication of competencies to other parts of the firm. Causal Ambiguity is the situation where it is hard or even impossible to relate the consequences or effects of a phenomenon to its initial states or causes.
The ability to transfer knowledge within a firm allows it to replicate practices in other parts of the organization. In other words the factors responsible for firm performance may be difficult to identify because of causal ambiguity. One area were this phenomenon is well known is the development of the prices of shares options futures and similar products on exchanges picture.
Porter causal ambiguity can be described as a combination of conscious planned and unconscious unplanned activities practices rituals work habits cultures and rules which result in an organization being successful. According to renowned Harvard Professor Michael E. As a central construct in strategic management causal ambiguity constrains a firms ability to replicate valuable capabilities internally yet simultaneously offers a means of protecting those capabilities from imitation by external agents.
Reinvestment in causally ambiguous competencies is necessary to protect the advantage. Lippman. Causal ambiguity describes a lack of understanding of cause-and-effect interactions between resources and competitive advantage.
Causal ambiguity means that the cause cannot be related to the effect. Definition of causal ambiguity. However some scholars argue that there was evidence for a fragmentary.
The resource-based view RBV is a managerial framework used to determine the strategic resources a firm can exploit to achieve sustainable competitive advantage. Causal ambiguity limits competitive imitation because competitors do not know the underlying reasons for a rival firms effectiveness and so they cannot identify what they should be imitating. Explanations of a major impediment to knowledge transfer.
Causal ambiguity refers to ambiguity perceived by organizational decision makers as to how organizational actions and results inputs and outcomes or competencies and advantage are linked King 2007. Ambiguity means sometimes you will make the wrong decision. It is central to.
Https Www Jstor Org Stable 20159191

Internal Analysis Resources Capabilities And Activities By Cecilia Christine And Savanna Stockpile Ppt Video Online Download
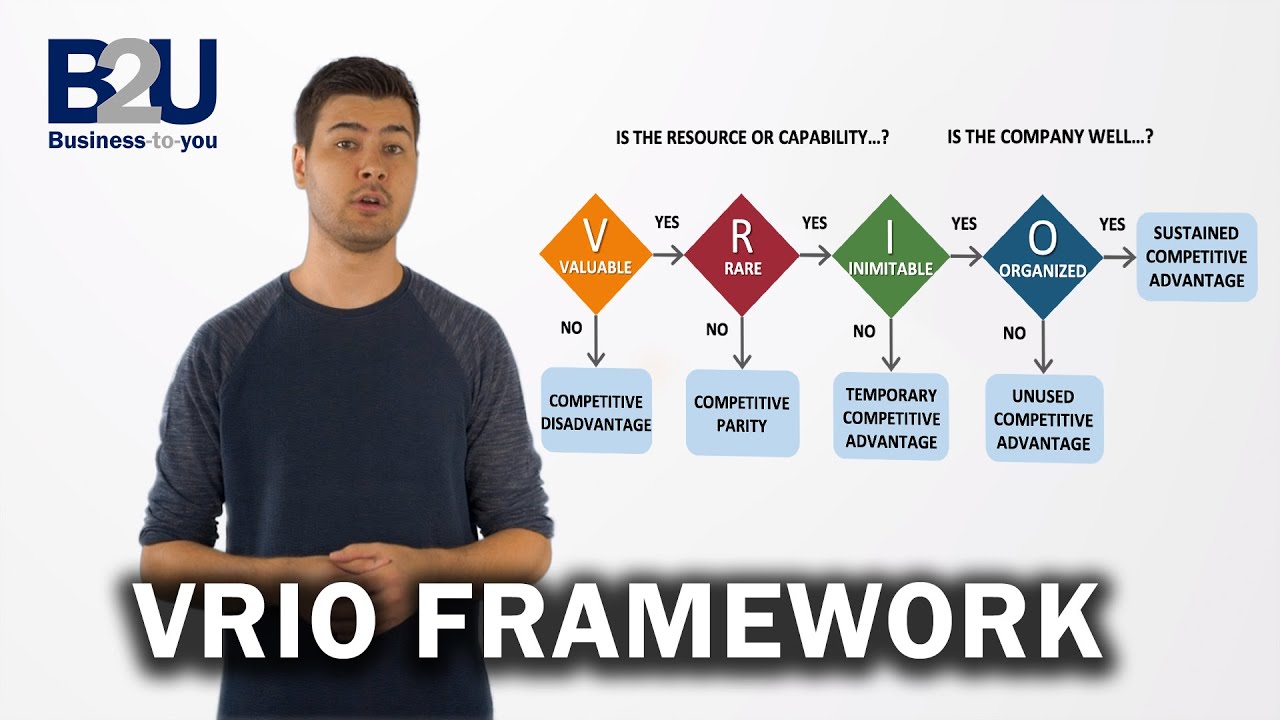
Vrio Framework Explained With Examples B2u

Vrio Framework Explained With Examples B2u

Apple S Sustainable Competitive Advantage
The Systems Thinker Fine Tuning Your Causal Loop Diagrams Part I The Systems Thinker
Msm 6650 Strategic Management Flashcards Quizlet

Pdf Determinants Of Causal Ambiguity And Difficulty Of Knowledge Transfer Within The Firm

Pdf On Uncertainty Ambiguity And Complexity In Project Management Semantic Scholar

Vrio Framework Explained With Examples B2u
Https Www Jstor Org Stable 2635212
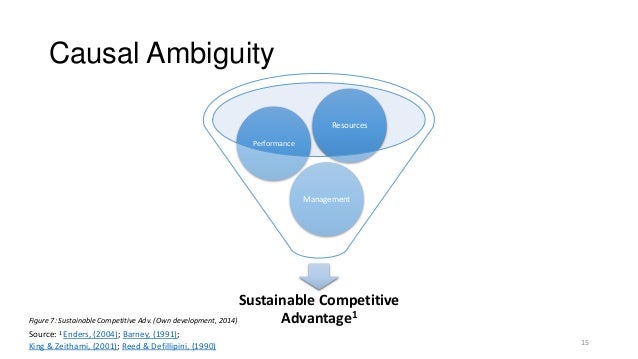
Apple S Sustainable Competitive Advantage

Msm 6650 Strategic Management Flashcards Quizlet
If Managing Knowledge Is The Solution Then What S The Problem

Pdf Determinants Of Causal Ambiguity And Difficulty Of Knowledge Transfer Within The Firm

Leading Through Vuca Volatility Uncertainty Complexity And Ambiguity By Pamela Meyer Ph D Medium

Internal Environment Assessing The Internal Environment Of The Firm C Hapter Ppt Download



Posting Komentar untuk "Causal Ambiguity Definition Business"